Factory Method Pattern
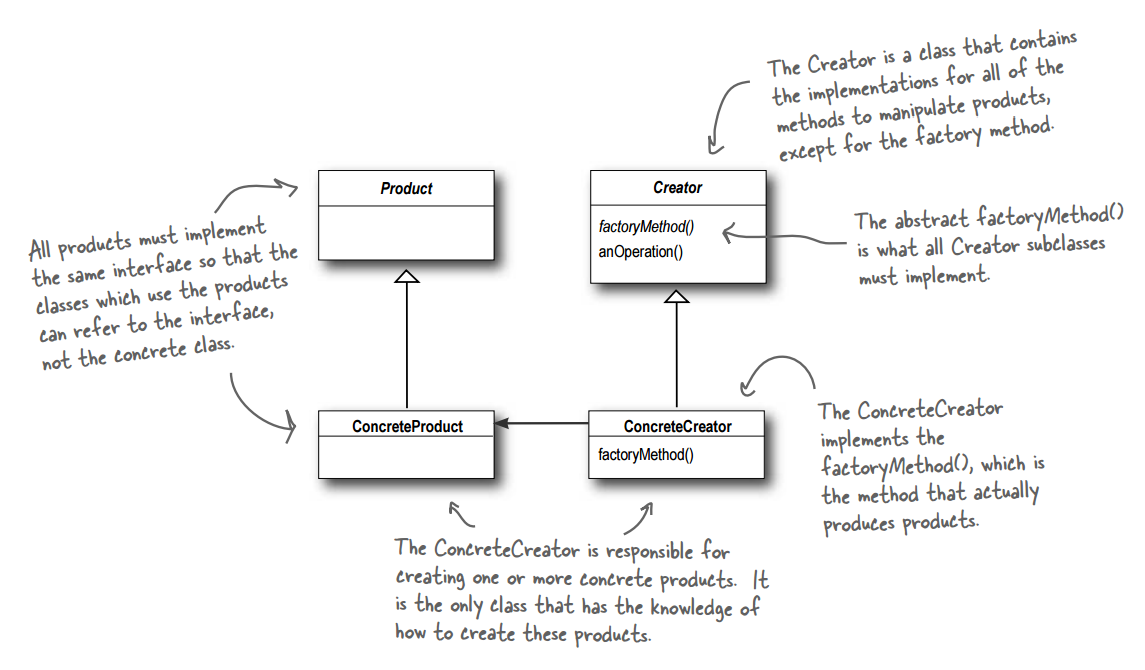
The Factory Method Pattern defines an interface for creating an object, but lets subclasses decide which class to instantiate. Factory Method lets class defer instantiation to subclasses.
Factory Method relies on Inheritence: object creation is delegated to subclasses which implement the factory method to create objects.
A factory method handles object creation and encapsulates it in a subclass. This decouples the client code in the superclass from the object creation code in subclass.

Advantages :
- Factory method eliminate the need to bind application-specific classes into the code. The code only deals with the product interface, that way we are decoupling the implementation of the product from its use, therefore it can work with any user-defined ConcreteProduct classes.
- It gives subclasses a hook for providing extended version of the object.
- Connects parallel class hierarchies : It encapsulates product knowledge into each creator.
Example
public abstract class PizzaStore {
public Pizza orderPizza(String type){
Pizza pizza;
pizza = createPizza(type);
pizza.prepare();
pizza.bake();
pizza.box();
return pizza;
}
protected abstract Pizza createPizza(String type);
}
public class NYStylePizzaStore extends PizzaStore {
Pizza createPizza(String type){
switch(type){
case "cheese":
return new NYStyleCheesePizza();
case "veggie":
return new NYStyleVeggiePizza();
default:
return null;
}
}
}